Cancer is a disease due to which cells in the body grow out of control and misbehave. When the cells of the lungs get infected and process the damage to the lungs is called lung cancer. Lungs cancer may spread to lymph nodes and other organs in the body. Lungs cancer can also be caused by the other organs of the body. When the cancer cells spread from one to another organ it is said to be metastases.
What is Lung Cancer | Stages of Cancer | Dr. Virendra Singh
Lung cancer is of two types: –
● Non-cell lung cancer
● Small cell lung cancer
Both types of cancer grow in
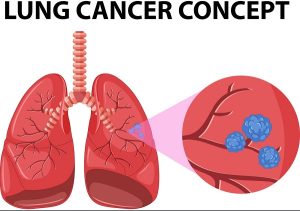
different ways and are also treated differently. Non-small cancer is common as compared to small cancer. Mainely cancer is caused due to smoking. Cigarette smoke contains all the substances due to which cancer is caused and it affects the lungs with immediate effect. Doctors believe that smoking damages the active cells which line the lungs. In starting, maybe your body gets the ability to repair the damage. Over time the damage can be the reason for the abnormal behavior of cells.
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
It is estimated that 80% to 85% of cancers are non-small cell cancer. The main subtype of non-small cell cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. These all subtypes have similar prognoses and treatment. The Adenocarcinomas
Adenocarcinoma: – The Adenocarcinomas process in those cells which normally secrete substances such as mucus. This is the type of lung cancer that mainly occurs in people who smoke.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: – Benign Growths Cancer Squamous cells are the origin of carcinoma. These are flat cells that are found inside the airways in the lungs. They are to be found in the central part of the lungs, near the main airways.
Large cell carcinoma: – This is also called large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma and it can appear in any part of the lungs. It grows fast and spreads quickly and is harder to treat. It is fast-growing cancer that is very similar to small cell lung cancer.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
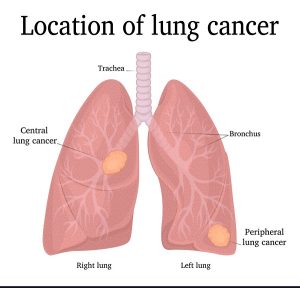
Small cell cancer accounts for roughly 10% to 15% of all malignancies, according to estimates. Oat cell cancer is another name for it.This type of cancer grows and spreads faster as compared to non-small cell cancer. It is more dangerous as compared to other types of cancer.
Stages of lung cancer
Stages of lung cancer are classified as three factors as TNM systems. A combination of all of these elements determines the cancer stages.
● T: – Tumor size and location.
● N: – Regional lymph involvement. The lymph nodes, which are shaped like tiny balls, transfer immune system organs throughout the body.
● M: – Metastasis status.
Non-small cell lung cancer stages
Non-small cell cancer stages are from the range of one to four. Stage 0 is the earliest stage of cancer. It is present in the top lining of the lung or bronchus.
Stage 1st: – Stage 1st of non-small cell l cancer is divided into 2 parts. 1A and 1B, it is based on the size of the tumor.
Stage 2nd: – Stage 2nd is also divided into stage 2nd A and 2nd B. These tumors are larger as compared to the 1st stage. It spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Stage 3rd: – Stage 3rd of non-cell cancer is classified into 3A, 3B, and 3C. It depends on the tumor’s size and location.
Stage 4th: – The 4th stage is the most advanced form in Non-small cell cancer (NSCLC). In the 4th stage, cancer spread to the lining of the lung.
Small Cell Lungs Cancer Stages
There are two stages of small cell cancer: limited and widespread.
● Limited stage: – Small Cell Lungs Cancer limited-stage is the only stage in which only one lung with or without spreads to lymph nodes in the area between chest and lungs.
● Extensive stage: – In this stage, it spread to tissues outside of the originally affected lungs.
Dr. Virender Singh is one of the best and most experienced doctors. He is an expert to treat lung cancer. Under him, one will get the best treatment as he well understands the health issues related to the lungs. To know more visit: – drvirendersingh.com