Pulmonary Edema, also known by other names such as wet lung, lung water, Lung congestion or Pulmonary congestion, is a condition when excessive fluid gets fill in the air sacs of the lungs which makes it difficult to breathe. It can be acute or chronic i.e., it might occur suddenly or can establish itself with time. Accumulation of fluids in the air sacs leads to shortness of breath. Congestive heart failure often causes pulmonary edema. The veins that carry blood through the lungs can back up if the heart cannot pump efficiently. Fluid is forced into the lungs’ air sacs (alveoli) as the pressure in these blood vessels rises. This substance reduces the oxygen of the lungs. Combined, these two elements contribute to breathless.
Consult Dr. Virendra, the leading chest expert in India. Dr. Virendra Singh is the best chest and asthma expert in India. He is consider a pioneer in the field of respiratory diseases.
What is Pulmonary Edema? Symptoms and causes
Pulmonary edema. Fluid in the respiratory organs.
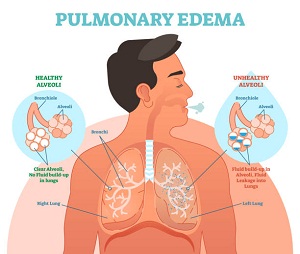
Causes: Usually, in the lungs, alveoli present are filled with air for the exchange of gases. Through these alveolar sacs oxygen is taken up by the tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues is exhale out from the body. But, in Edema, lungs get flood by fluids reducing the movement of oxygen in the lungs. Dr. Virendra says, Pulmonary Edema is sometimes cause by congestive heart failure, during which the heart is unable to pump blood efficiently. Due to decreased efficacy of the heart, blood can remain reserved in the veins. This backed-up blood finds its way to the lungs where it gets accumulated in the alveoli. This contained blood causes the following effects:
* difficulty in breathing.
* bloodstream cannot get enough oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide become difficult.
Other possible causes of Pulmonary Edema include:
- Trauma
- Pneumonia
- Blood infection
- Liver cirrhosis
- Direct injury to lungs or inflammation in other parts of the body.
Symptoms: Depending on acute and chronic conditions, symptoms might differ. Acute pulmonary Edema shows severe indications whereas in cases of chronic Edema, symptoms appear when the conditions last in the body for a long time, and are less severe.
In cases of acute pulmonary Edema, symptoms include:
- Coughing with pink sputum
- Congested chest
- Restlessness
- Chest pain
- Anxiety
- Palpitations
In chronic cases of Edema, symptoms can be:
- Difficulty in breathing with some physical activity
- Swelling or Edema of legs or feet
- Episodes of dyspnea at night
- Tiredness
- Orthopnea
Consult the best specialist for precision and correct treatment.
Diagnosis: Dr. Virendra suggests diagnosis includes a physical examination followed by routine examination and tests. Abnormal rhythms and crackling sounds in heartbeats can be heard using a stethoscope. The activity of the heart can be determine by an echocardiogram. Also, the doctor may advise an X-Ray or ultrasound of the lungs to check the presence of fluids inside or around the lungs, also to check the size of the lungs. CT scan may also be useful to rule out the actual condition of the lungs. Treatment for patients with this disease is based on the patient’s history, examination and test results.
Conclusion: Pulmonary Edema can be fatal if not treated on time and can cause major breathing difficulties in patients suffering from the same. When a person is suffering from Edema it is necessary to provide immediate attention and the best treatment possible. Certain precautions need to be taken care of to prevent Edema conditions such as prevent high cholesterol conditions in our body, controlled salt intake, and cessation of smoking habits so that there is no direct injury or damage to our respiratory passage. Consult Dr. Virendra singh for assistance and the best treatment.
